While the Trilogue discussions on the Solvency II review have just begun, Addactis experts offer you an analysis of the Pillar 1 key issues, a reminder of the genesis of the review and the ongoing legislative process in order to provide visibility on the next steps.
In this article, you will find these 5 key points that are still under review:
Solvency II reviews
Solvency II Directive, which came into effect on the 1st of January 2016, already included two review clauses in its texts:
- In 2018, a review of the sole delegated regulation (level 2).
- In 2020, a full review including the directive (level 1) and the delegated regulation (level 2).
Legislative process of the 2020 Solvency II Review
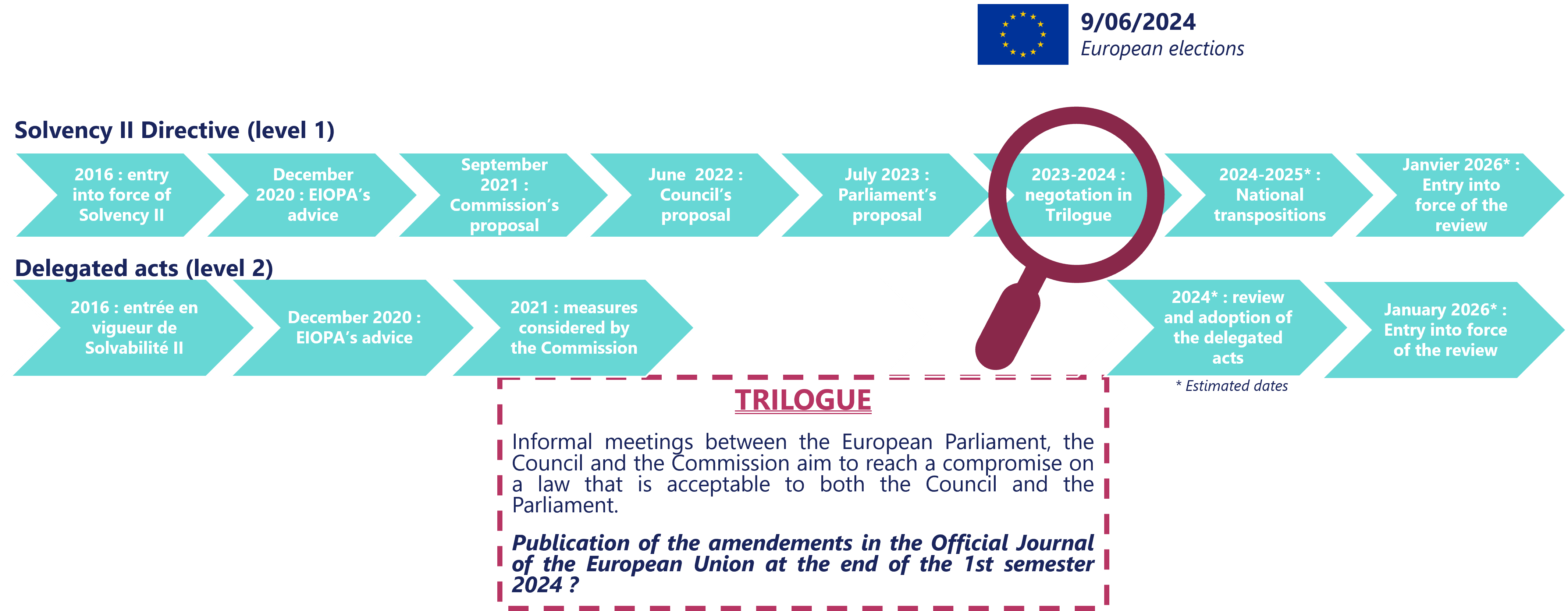
In July 2023, the European Parliament adopted its proposal for the Solvency II review, one year after the European Council. The Level 1 review is now entering its final phase: the trilogue discussion.
The trilogue’s ability to find an agreement before the European elections in June 2024 and the renewal of the European Parliament will be crucial to the timeline for the next steps of the review (transposition into national law and adaptation of the delegated regulation).
Pillar 1 in the 2020 Solvency II Review: 5 Key Issues
1. Extrapolation of the Risk-Free Interest Rate Curve
Objective: Take into account market data (liquid) beyond the first extrapolation point, resulting in a better estimation of the best estimate.
Issues:
- First Smoothing Point (FSP)
It should have a function equivalent to the current Last Liquid Point (LLP) under Solvency II. The date on which it will be calculated is still under discussion. The option to select a date beyond 20 years as LLP date is being considered.
- Volatility Adjustment (VA)
It could be added on the top of the extrapolated part of the curve.
- Liquidity
It could play a central role in setting the FSP, whereas it has a less prominent role in the current standard.
- Convergence Parameters
The speed of the convergence towards the UFR can have significant effects. It will directly impact the curve’s shape beyond the FSP and, consequently, the assessment of future liabilities and profits.
2. Volatility Adjustment
Objective: Redefine the VA to better mitigate the impact of observed spread movements on the insurance liabilities.
Issues:
- Reference Portfolio Composition
It would no longer include equity and real estate assets but only debt instruments.
- Application Ratio
The proposal is to increase it from 65% to 85%.
- Credit Spread Sensitivity Ratio (CSSR)
This is an additional ratio which would be applied to the VA and would accounts for the duration and volume gaps between an insurer’s assets and liabilities, potentially making the VA entity-specific.
- Macro-Economic VA
It would be a reshaped national component of the VA with a smoothed activation to mitigate the current threshold effects.
3. Risk Margin
Objective: To consider the decreasing risk dependency over time, reducing the risk margin sensitivity to interest rate volatility.
Issues:
- Introduction of a time-dependent parameter
The introduction of an exponentially decreasing parameter λt aims at introducing a risk dependency evolution over time. Its value, presumably between 0.5 and 1, will drive the decreasing speed.
- Cost of Capital, CoC
Various proposals to lower the cost of capital from 6% to 5% or 4.5%, aligning with the time-dependent parameter to lower the risk margin.
4. Standard Formula: Interest Rate SCR
Objective: to better consider the recent environment of low/negative interest rates.
Issues:
- Increased Capital Requirements
Significant amplification of both upward and downward shocks – introducing shocks to negative rates – in low-interest-rate environments, lower amplification in a higher interest rate environment.
- Risk Correlation
The correlation between spread risk and interest rate down SCR would change from 50% to 25%.
- Extrapolation
Potential introduction of an extrapolation from the shocked liquid part of the interest rate curve to a shocked UFR (+/- 15 bps)
- Transitional Phase
Potential smoothing of the SCR increase over five years.
5. Standard Formula: Equity SCR and Dampener
Objective: Give insurers a higher capacity to contribute to the long-term financing of economic entities.
Issues:
- Criteria for the eligibility to Long-Term Equity Investments (LTEI)
Revised criteria for LETI qualification to expand the eligible asset base, targeting SMEs and infrastructure companies/projects.
- Duration-based sub-module
Removal of the equity risk sub-module based on duration.
- Equity Dampener
Increase the upper and lower bounds of the dampener from +/- 10% to +/- 17%, enhancing the counter-cyclical effect of the measure.
Solvency II review: anticipating the changes ahead
The ongoing Solvency II review is expected to result in significant changes for both L&H and P&C stakeholders (risk margin, interest rate SCR, LTEI, and equity dampener), and other focused on long-term guarantees (interest rate curve extrapolation and volatility adjustment).
Addactis experts are available to assist in understanding the technical issues, the different positions of co-legislators, and the potential implementation timeline.
Contact us to better understand how to tackle Solvency II challenges within your organisation.
This article is written by:

Ange BOUYOU-MANANGA
Senior Manager – Actuarial Consulting

Elie MERYGLOD
Senior Manager – Modeling & Finance Life & Health

François BAYÉ
Director, Deputy Head of Actuarial Consulting

Simon THIBAULT
Senior Manager – Modeling & Finance Life & Health
Find previous articles related to this subject:
2020 Solvency II Revision: Anything new during the summer?
n June 2022, the ECON committee of the European Parliament began discussions on the Solvency II revision. What is the current status today?

EIOPA discussions about the prudential treatment of sustainability risks
Addactis experts guide you in the understanding of the latest EIOPA regulatory texts on climate risks.

EIOPA: Natural Disasters & Insurance Protection
Faced with the shortfall in NAT CAT insurance protection, EIOPA has decided to introduce a dashboard, which main objective is to monitor the risks associated with these protection gaps. Take a closer look with our experts!