Ensuring data accuracy and integration from multiple sources is a significant challenge for actuaries and financial teams. These challenges must be addressed to achieve transparency in financial results.
This article discusses the key data challenges under IFRS 17 and offers solutions for successful implementation and data quality.
IFRS 17 Overview
The implementation of IFRS 17
Keys elements such as Revenue and liability recognition, Evaluation of obligations, CSM, Contract grouping introduce a new level of complexity.
However, this shift also enhances transparency and comparability in financial reporting with a focus on cash flows and more detailed financial disclosures.
IFRS 4 vs IFRS 17

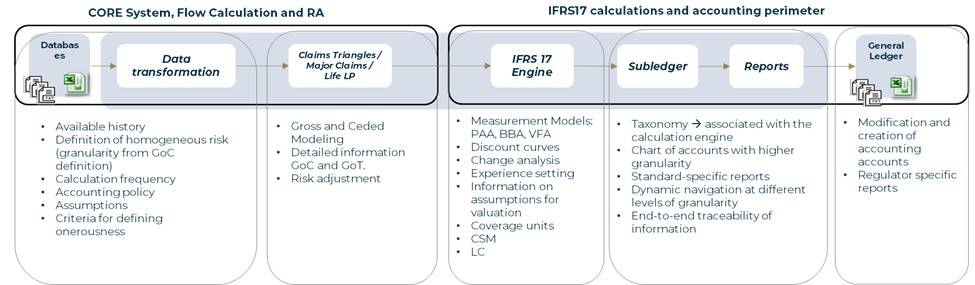
The role of data in IFRS 17
It requires complex data processing and transformation of projections; It generates complexity due to the lack of a clear definition of how certain calculations should be performed (non-prescriptive = methodological decisions) and the lack of the necessary granularity in the data.
It implies a strong integration between systems and areas of the company, as well as a significant impact on run times and storage capacity.
Type of data required
Data Management
1. Storage
2. Treatment
3. Analysis
Data-related challenges
Data complexity: Diversity and volume of data to be managed
- Required level of granularity (policy level) with a requirement for traceability from start (source) to end (reporting).
- Different formats, Empty data, Data in the user’s machines and/or different systems per area.
- Understanding of data and new criteria, Reviews are required from start to finish of the process, there is no single responsible party.
- Change of methodologies (current vs IFRS17) and this does not make the data comparable.
- Different currencies (functional vs. reporting). Structure of the one being taken to OCI or P&L.
Systems integration
Regulatory compliance and data security
|
IFRS 17 Compliance
|
Data Security
|
Solutions and best practices for Data Management
Technologie and tools
Use of software and data management tools
- Best practices: Data structured in the same way to make report generation easier. E.g. Same date format
- Repository: Avoid having the data on the computer, but on an internal corporate network. Organization of data repository E.g. Established formatting rules
- Data management tool: The most common tool is Microsoft Excel, but unless you have programmed macros, it is very difficult to check automatically.
- Software usage: It would be ideal to have a software, understanding the capacity of the company. Keys: data management support, Information management, Organization and Traceability.
Data governance
Implementation of policies and procedures for data management
Data Processing: Establish policies prior to analysis. What procedures do I have defined? Who performs reviews? Who gives the go for the next step?
Training and awareness
Importance of training teams in data management
- Teams must know the why and why not of the importance of data quality.
- Awareness of the effects of the process, from the beginning to the end.
- What does your participation involve?
- Importance of verification.
- If there are defined structures, human error is reduced, it helps to ensure good data quality.
Why improving data management
A structured and well-defined system and/or process allows the traceability of information from start to finish and at the required level of granularity, as this is relevant in obtaining reliable and consistent results.
Having an information management process is important to avoid errors in the data that may lead to the presentation of results that reflect incorrect figures to the market.
Training teams on the standard is not only essential to validate the reliability of the results, but also to understand the company’s financial situation and the variables that have the greatest impact (e.g., estimation assumptions, variation in discount curves, cash flow, etc.).
The quality and accuracy of the data are essential to accurately reflect the financial situation of the insurers.
Implementing effective data management practices enables insurers to comply with IFRS 17, ensuring accurate calculations and informed decisions and optimizing their operations.
Ensuring data quality not only meets the requirements of IFRS 17, but also strengthens strategic decision making within the organization.
Related content on IFRS 17

Mutualidad renews its trust in Addactis through its IFRS 17 project
Mutualidad renews its trust in Addactis through its IFRS 17 project. Read more about this insurance company’s experience.

Data, systems integration, processes, reporting…: The Strategic Role of Finance in IFRS 17
In the rapidly evolving insurance industry, finance and accounting teams are essential drivers of operational improvement and regulatory compliance. Discover our article about the Strategic Role of Finance in IFRS 17.

Key Considerations for a Smooth IFRS 17 Implementation
Discover the critical steps insurers must take for a successful IFRS 17 implementation, including gap analysis, data readiness, and system upgrades.


 < onerror="this.style.display='none'" />
< onerror="this.style.display='none'" />
